 Operations Management (OM) is simply the management of systems or processes that convert or transform resources into goods and services. Essentially, it is responsible for managing the core processes used to manufacture goods and produce services, and as explained by the MIT Sloan School of Management, ranges across a business's strategic, tactical and operational levels.
Operations Management (OM) is simply the management of systems or processes that convert or transform resources into goods and services. Essentially, it is responsible for managing the core processes used to manufacture goods and produce services, and as explained by the MIT Sloan School of Management, ranges across a business's strategic, tactical and operational levels.Explain operations management’s role in business
OM has many roles in business including that of;
- Forecasting
- Capacity Planning
- Scheduling
- Managing Inventories
- Assuring Quality
- Motivating and Training Employees
- Locating Facilities
Describe the Correlation Between Operations Management and Information Technology
A strong relationship exists between both operations management and information technology, with IT exerting a significant influence over OM decisions. One of the greatest benefits IT gives to OM is its ability to assist in the operational decision-making process. With the many possible alternatives that often exist and the varying impact each of these can have on company revenue and expenses, it is often critical that managers are able to make informed decisions.
It is in this way that IT in the form of Decision Support Systems and Executive Information Systems can provide an organisation with sound forecasting tools in the way of What-If Analysis, Sensitivity Analysis, Drill-down and Consolidation. By doing this, IT assists OM by providing managers with strong information that helps them make good decisions by answering the questions of;
Explain Supply Chain Management and Its Role in a Business
Supply Chain Management is the management of information flows between and among stages in a supply chain to maximise its effectiveness and profitability. In this way, the role of Supply Chain Management is essentially that of an enabler. When it is utilised in an effective and efficient manner it allows an organisation to;
- Decrease the Power of Buyers
- Increase its own Supplier Power
- Increase Switching Costs to Reduce the Threat of Substitute Products or Services
- Create Entry Barriers that Reduce the Threat of Substitute Products or Services
- Increase Efficiencies while Seeking a Competitive Advantage through Cost Leadership
List and Describe the Five Components of a Typical Supply Chain
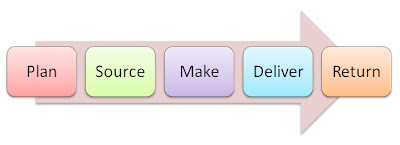
As seen in the diagram above, the 5 main components of a typical supply chain are;
- Plan
- Source
- Make
- Deliver
- Return
Define the Relationship between Information Technology and the Supply Chain
As companies and the corporate environment as a whole continue to evolve, the idea of virtually seamless information links within and between organisations has become an essential element of integrated supply chains. It is in this way that the role of information technology has become increasingly valuable to the supply chain.
Essentially, the primary role of IT within the supply chain is to create integration and information linkages between both functions within a firm and between firms. This allows smooth and synchronised flow of information across the chain and also integrates planning, decision-making processes, business operating processes and information sharing for business performance management.
It is in this way, that Information Technology has made it possible to bring the idea of true supply chain integration to life. This can be seen in Adaptec Inc’s use of supply chain integration software over the internet to synchronise their planning.



No comments:
Post a Comment